The fluid balance chart (figure 1) is an essential component of fluid monitoring and should inform fluid prescribing and/or clinical interventions related to fluid loss or overload. the fluid balance chart is used to record the patient’s fluid input and output over a 24 h period at the end of which the total input and output is calculated to. Recommendations are made to improve fluid balance management in clinical complete a fluid balance chart accurately, recognising when fluid intake or . To to ensure that fluid balance charts are completed adequately for clinicians to compose safe management plans for patients. this is a retrospective audit against a standard adapted from an nhs trust guideline. the standards audited against were (1) oral fluids to be documented in ml, (2) iv.

More fluid balance chart clinical guidelines images. The three elements to assessing fluid balance and fluid balance chart clinical guidelines hydration status are: clinical assessment, body weight and urine output; review of fluid balance charts; and review of blood chemistry. fluid balance recording is often inadequate or inaccurate often because of staff shortages, lack of training or lack of time.
Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best Ncp Dehydration
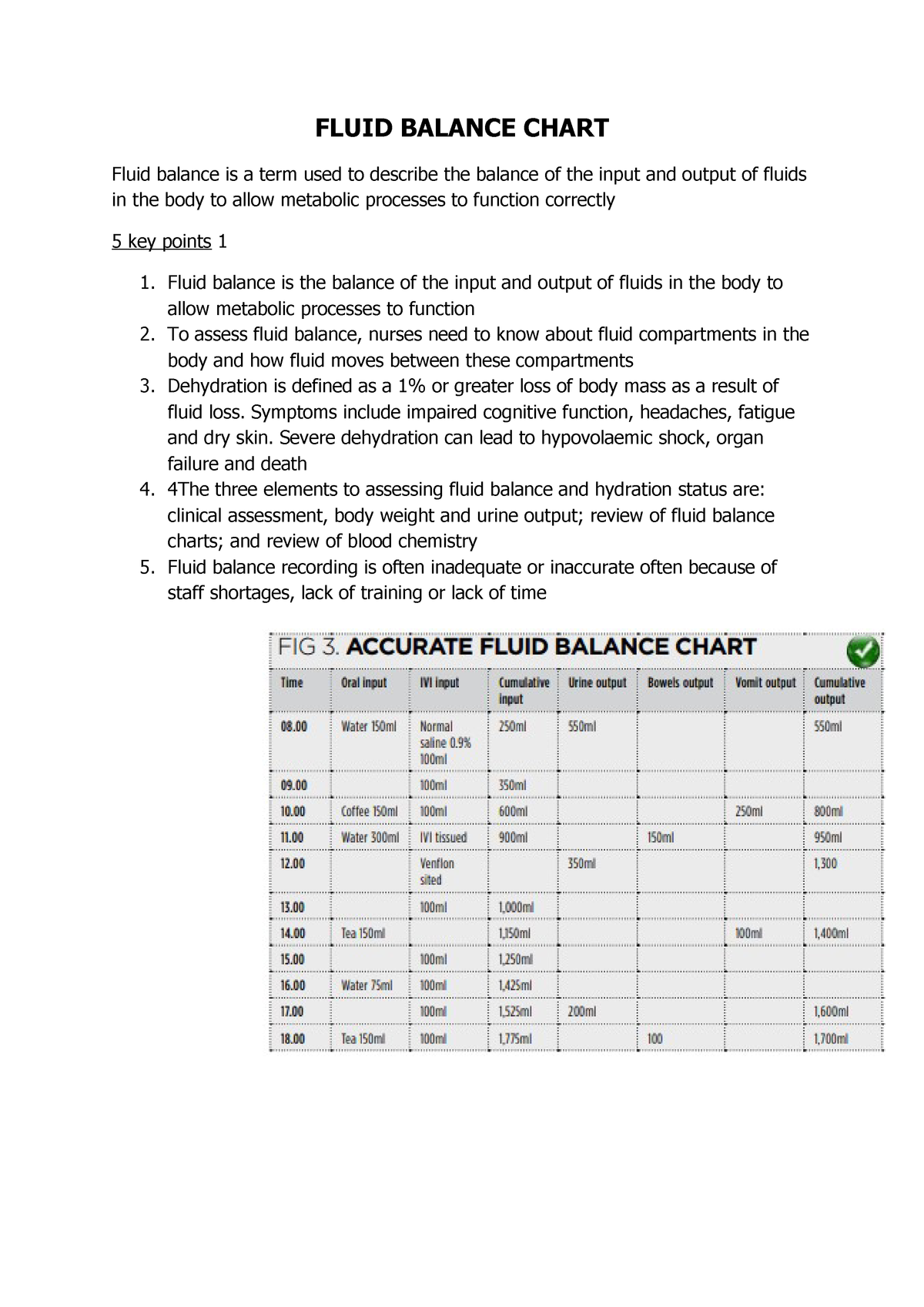
Jul 15, 2011 · how frequently the fluid balance chart data should be recorded such as hourly or two hourly should be clearly documented. it is not acceptable practice to use shorthand. fig 3 shows best practice when completing a fluid balance chart and fig 4 shows an example of unacceptable practice (smith and roberts, 2011). Page 2 of 7 guidelines for the recording of fluid balance / intake output. table of the patient, careful examination and clinical observation and an understanding measure all intake and output on the trust's fluid balance ch.
Improving Fluid Balance Monitoring On The Wards Bmj Open

Clinical Practice Guidelines Diabetes Insipidus
Guidance. fluid balance is a term used to describe the balance of the input and the gold standard is for all patients to have a completed fluid balance chart that the medical team will require an accurate 24 hour total to inform c. Download ebook fluid balance chart guidelines clinical situation stretch activities challenge you with more nuanced, fluid balance chart clinical guidelines advanced issues to reflect upon many of the features in the book are relevant to trainee nursing associates, especially when used in conjunction with supervision from academic and clinical teachers.
Change in weight as marker of fluid status baseline investigations should include urea and electrolytes, full ward test of urine and paired serum and urine osmolality. diabetes insipidus is present when the serum osmolality is raised (>295 milliosmol/kg) with inappropriately dilute urine (urine osmolality <700 milliosmol/kg). All fluid balance charts must be accurate assess the patient's likely fluid and electrolyte needs, clinical history, previous intake, thirst, abnormal 5% contains 5g/100mls) for special considerations refer to nice guidelines.
Fluid Balance For Adult Inpatients Clinical Guideline V1 0
Clinical experience and nursing metrics have consistently identified poor documentation of fluid balance monitoring at milton keynes university hospital, compromising patient safety and quality of care. this project aimed to increase the percentage of fluid balance charts correctly completed on the wards. three areas for improvement were identified: understanding the importance of good fluid. Benjamin franklin frs frsa frse (january 17, 1706 [o. s. january 6, 1705] april 17, 1790) was one of the founding fathers of the united states. a polymath, he was a leading writer, printer, political philosopher, politician, freemason, postmaster, scientist, inventor, humorist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat. 2. 4 when to review and/or stop a fluid balance chart when patients are transferred to other wards / departments, a verbal and written handover must include whether the patient is on a fluid balance chart fluid balance charts must be reviewed in line with the patient’s clinical condition. Balance charts where appropriate and to bring any fluid balance chart clinical guidelines concerns to the attention of the rn and ahp in a timely manner. 6 policy statements assessment of hydration has three main elements: clinical assessment, review of fluid balance charts and review of blood chemistry. 5 6. 1 clinical assessment.
Sample Skill Elsevier Clinical Skills
Feb 28, 2019 commenced/discontinued on a fluid balance chart. nhs qis (2003) clinical standards for food, fluid and nutritional care in hospitals. A fluid balance chartis used to document a patient’s fluid input and output within a 24-hour period. this information is used to inform clinical decisions (such as medication and surgical interventions) from medical staff, nurses and dieticians, who all expect accurate figures in exact measurements (georgiades 2016).
May 16, 2020 a fluid balance chart is used to document a patient's fluid input and output within a 24-hour period. this information is used to inform clinical . Fluid balance charting is part of charting and managing clinical information and is therefore part of a nurse’s workload (nmba, 2016). as a result, time should be allocated during the shift to complete fluid balance charting. Feb 26, 2021 · fluid balance charts/weight charts; other losses (e. g. rectal bleeding) findings suggestive of hypovolaemia include: increased output from wounds and drains decreased urine output (<30mls/hr) a fluid chart showing a negative fluid fluid balance chart clinical guidelines balance; weight loss; other sources of fluid loss (e. g. rectal bleeding, diarrhoea, vomiting). Recommendations are made to improve fluid balance management in clinical complete a fluid balance chart accurately, when fluid intake or urine output is .
The nurse in clinical practice the thinking treatment = fluid intake. outcome of the chart gives me guidelines about the information i'm required to enter. D. encourage fluid intake up to 4000 ml every day. to decrease the risk for renal calculi, the patient should have a fluid intake of 3000 to 4000 ml daily. ambulation helps decrease the loss of calcium from bone and is encouraged in patients with hypercalcemia.
The target rate of serum sodium correction is 6-8mmol/l in 24 hours (unless seizingsee flow chart below). all children should have a strict fluid balance including weight (minimum daily, but maybe 6-12 hourly for more unwell children). remember to treat the underlying cause. *. Refeeding syndrome (see nutrition support in adults [nice clinical guideline ( urea, creatinine and electrolytes) and fluid balance charts, along with weight.
These guidelines were also updated in 2006. this recommendation was based on multiple clinical trials showing that the reduced osmolarity solution reduces stool volume in children with diarrhea by about twenty-five percent and the need for iv therapy by about thirty percent when compared to standard oral rehydration solution. Feb 08, 2013 · improving malnutrition and poor fluid management makes financial as well as clinical sense. 20 the national institute for health and clinical excellence has identified improvements in nutritional care as the fourth largest potential source of nhs savings. 2 a malnourished patient costs the nhs £2000 a year. 10 the cost of poor fluid management. Monitor intake and output, character, and amount of stools; estimate insensible fluid losses. measure urine specific gravity and observe for oliguria. provides information about overall fluid balance, renal function, and bowel disease control, as well as guidelines for fluid replacement.
Back to school: update medical records mayo clinic news network.
Benjamin franklin wikipedia.
8. when to stop a fluid balance chart fluid balance monitoring should only stop when the underlying reason for starting it has resolved, or the individual commences the end of life care pathway. each patient must be assessed thoroughly before stopping their fluid balance chart and it remains the clinical decision of a senior clinician or. The charting of fluid balance totals is open to error in the documentation of inputs is then reflected on the fluid balance chart. 14,17 an initial search of literature to extrapolate when making recommendations on clinical practic.